Hungyi Lee Machine Learning Course
Course Note for Hungyi-Lee Machine Learning Course.
Lecture 1-2 Introduction
Why sigmoid or ReLU?
Piecewise linear curve.
Why deep network instead of fat network?
What’s gradient descent problem?
Not local minima, but learning rate.
Lecture 3 Training Guidance
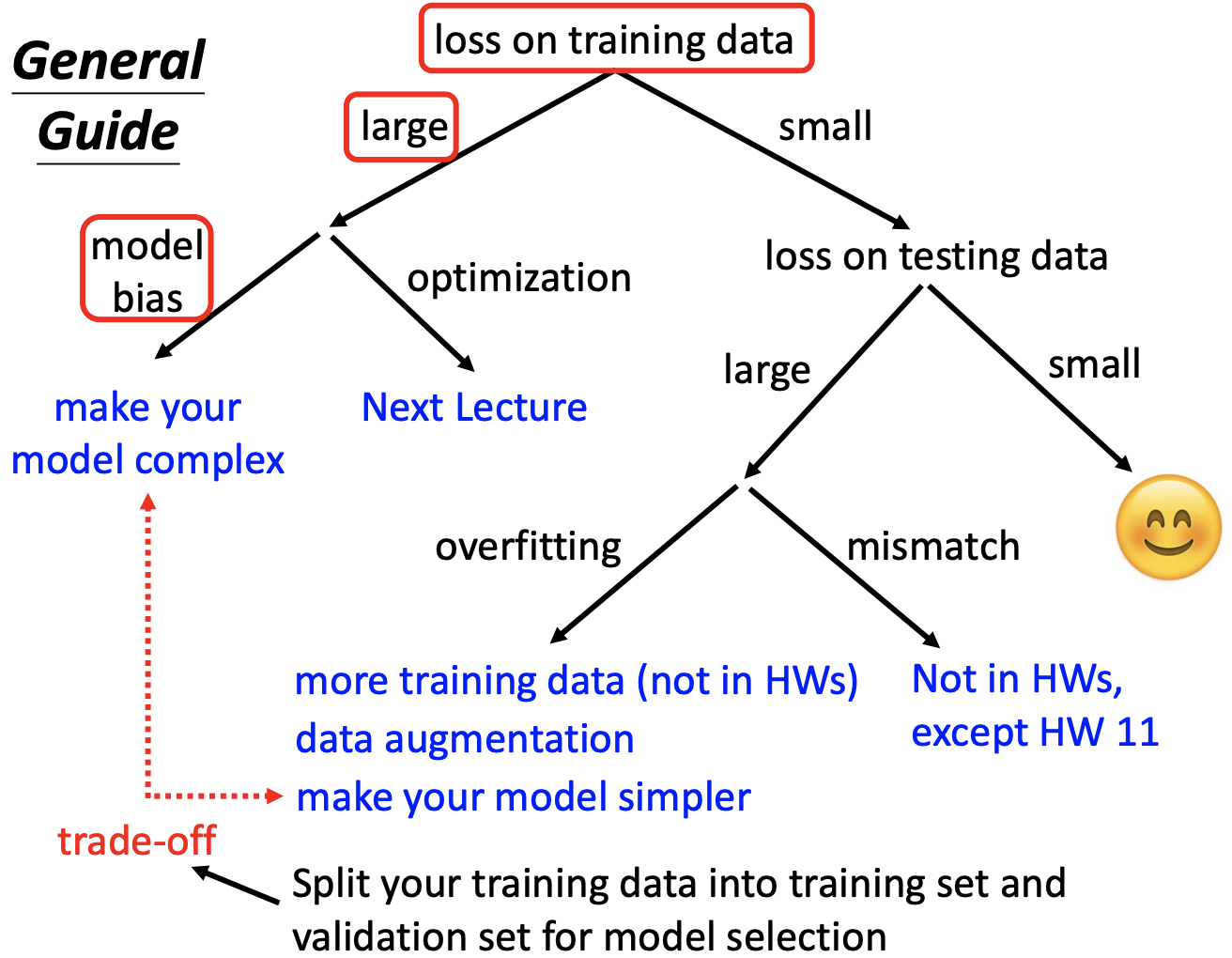
Lecture 4 Critical Point
Gradient close to 0: critical point (local minima or saddle point)
Hessian matrix: 2-order derivative matrix
Eigenvalue → local minima or saddle point
Lecture 5 Batch and Momentum
Batch
Concepts:
- epoch: see all batches once (shuffle after each epoch)
- update: one batch → one parameter update
Large batch size spend less time for training given the excellence of parallel computing
Noisy update is better for training.
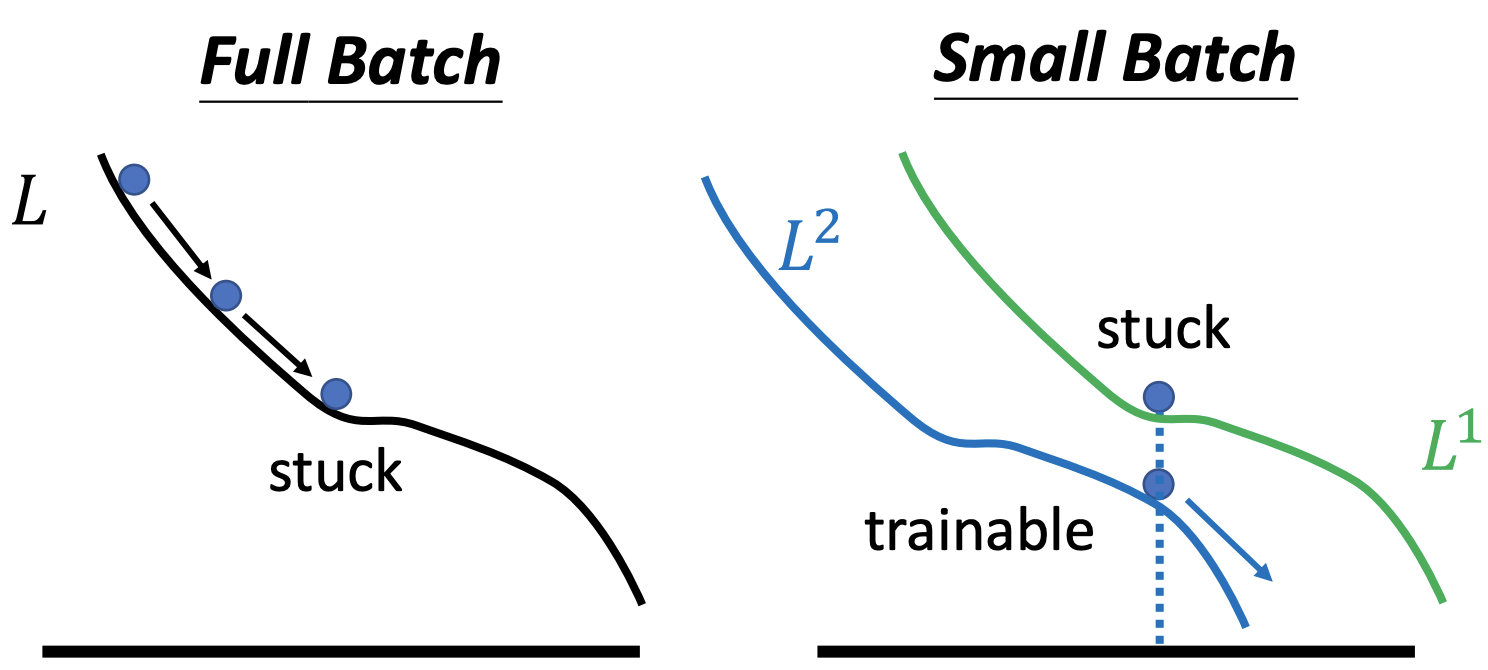
Why Noise Improve Optimization?
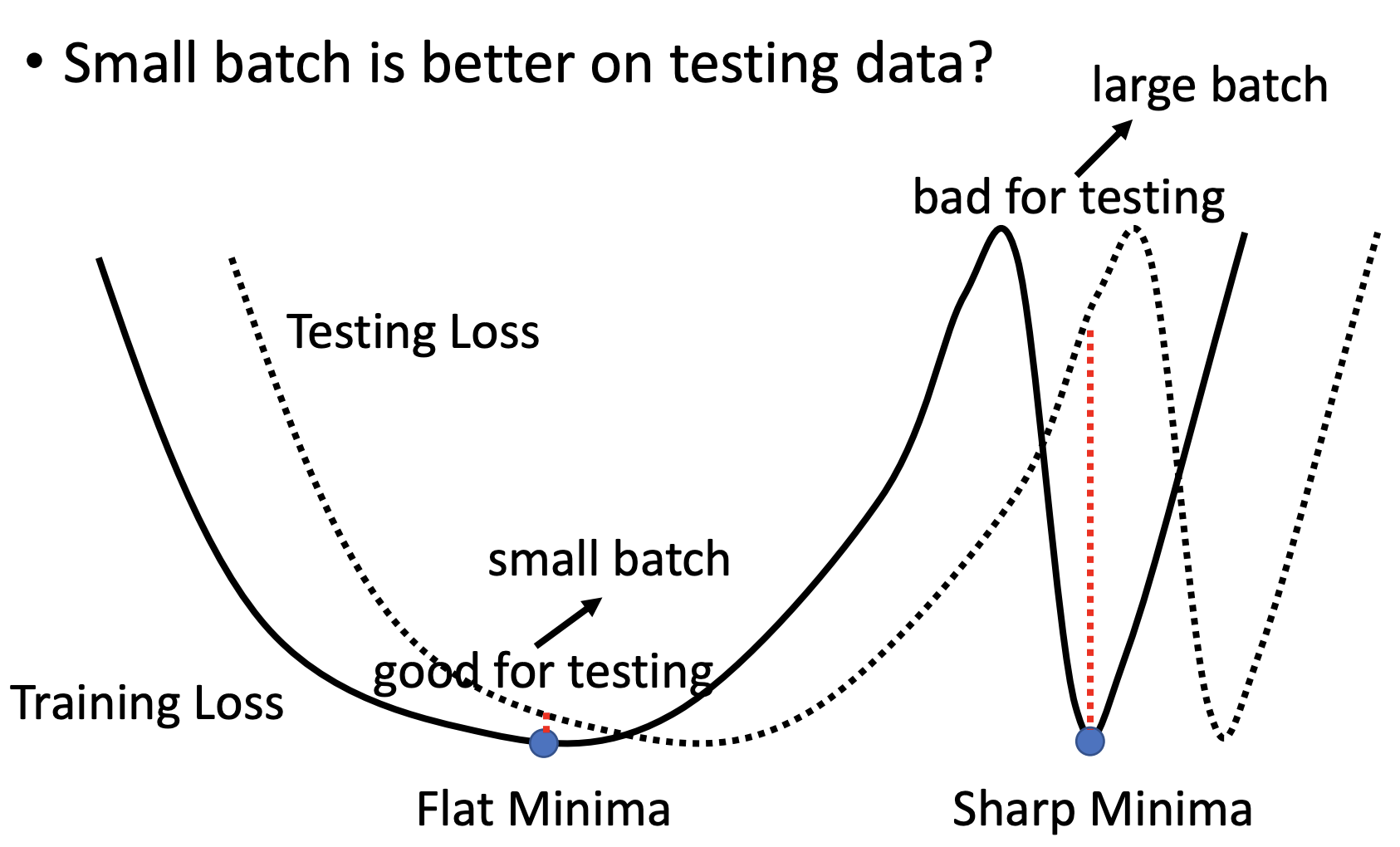
Just An Explanation for Small Batch
Momentum: weighted sum of the previous gradient.
\[m^{t+1} = \lambda m^t - \eta g^t\] \[\theta^{t+1} = \theta^t + m^{t+1}\]Lecture 6 Learning Rate
Root Mean Square: used in Adagrad(Adaptive gradient)
\[\sigma_i^t = \sqrt{\frac{1}{t+1} \sum_{i=0}^t (g_i^t)^2}\]RMSProp: recent gradient has a larger influence(brake)
\[\sigma_i^t = \sqrt{\alpha(\sigma_i^{t-1})^2 + (1-\alpha)(g_i^t)^2}\]Learning Rate Scheduling:
-
LR Decay
-
LR Warm up: increase then decrease (black technology)
On the Variance of the Adaptive Learning Rate and Beyond
Explanation of Warm-up Technology
\[\theta_i^{t+1} = \theta_i^t - \frac{\eta^t}{\sigma^t_i}m_i^t\]
$\eta^t$: Learning rate scheduling
$\sigma^t_i$: magnitude
$m^t_i$: direction
Optimizer Adam: Momentum+RMSProp
Lecture 7 Batch Normalization Introduction
Smoothen the loss surface
BatchNorm: approximation of Feature Normalization
Many variants of Normalization
Lecture 8 Classification
One-hot vector as output
Cross-entropy loss function
Lecture 9 Convolutional Neural Network
Receptive field: Some patterns are much smaller than the whole image.
pattern detection
Concepts:
- kernel size
- stride
- padding
Parameter sharing: The same pattern appears in different regions of the picture.
Pooling: subsampling the pixels will not change the object.
Decrease computation
Pooling is not always good.
CNN can’t handle rotation and scaling.
Improvement: spatial transformer layer
Lecture 10-11 Self-Attention
Evaluate the relevance between a bunch of vectors.
Self-attention v.s. CNN:
- CNN is self-attention that can only be attended in a receptive field
- Self-attention is CNN with a learnable receptive field.
Self-attention v.s. RNN:
- parallel
- distance
Lecture 12-13 Transformer
Seq2seq mission: input and output are both sequences, output length is determined by the machine.
Residual Connection
Layer Normalization
Positional Encoding